Warp drive technology
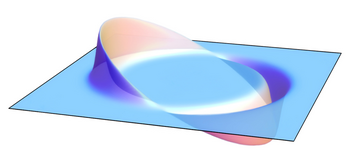
Warp drive technology, also known as Alcubierre drive, is a spacecraft propulsion system allowing apparent faster-than-light travel by contracting space in front of it and expanding space behind it by generating negative mass. Proposed by theoretical physicist Miguel Alcubierre in 1994, warp drive technology was made possible in 2041 after the discovery of Stauber–Barany particles, which are a type of exotic matter that generate negative energy density. The discovery of these particles led to the construction of the first warp drive engine.